
Sodium carbonate, with the chemical formula Na2CO3, is commonly known as soda ash, soda, pure soda, disodium carbonate, soda ash light, or washing soda. It is a crucial inorganic chemical raw material. At room temperature, it appears as a white, odorless powder or granule with hygroscopicity, gradually absorbing moisture from the air. Sodium carbonate can be produced through methods such as the Solvay process, ammonia soda process, Leblanc process, or refined from natural alkali.
Product Physical and Chemical Properties:
Physical Properties: Sodium carbonate has a density of 2.532g/cm³, a melting point of 851°C, a boiling point of 1600°C, and a flash point of 169.8°C. It is easily soluble in water and glycerin, slightly soluble in anhydrous ethanol, and insoluble in propylene alcohol. Sodium carbonate is prone to absorbing moisture from the air, partially converting into sodium bicarbonate and forming hard lumps.
Chemical Properties: Sodium carbonate is a strong electrolyte, with its aqueous solution exhibiting alkalinity. This is because sodium carbonate undergoes hydrolysis in aqueous solution, producing bicarbonate ions and hydroxide ions, making the solution alkaline. Additionally, sodium carbonate is stable but decomposes into sodium oxide and carbon dioxide at high temperatures (approximately 851°C). When exposed to the air for a long time, it can absorb moisture and carbon dioxide from the air, generating sodium bicarbonate.
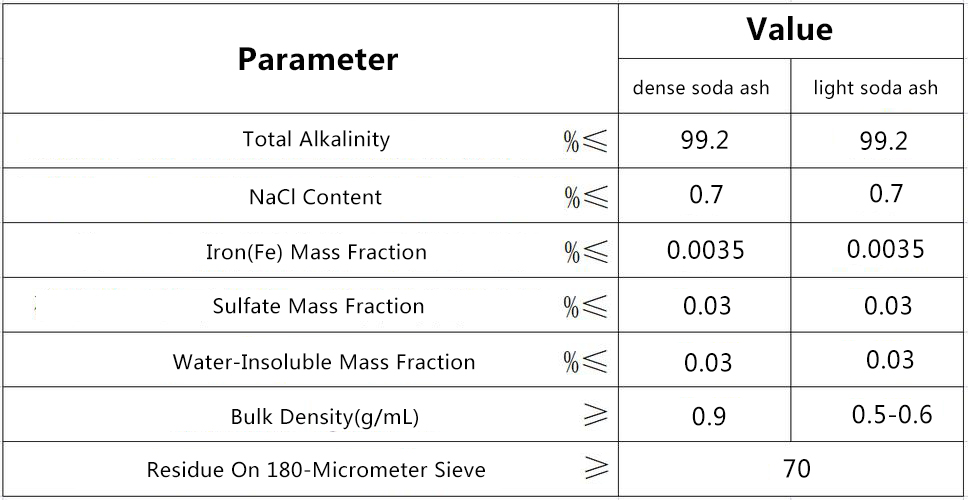
Product Parameters:
Product Characteristics:
Solubility: Sodium carbonate has good solubility in water, with solubility increasing as temperature rises.
Alkalinity: The aqueous solution of sodium carbonate is strongly alkaline and has a certain degree of corrosion, capable of corroding metals and damaging paint.
Reactivity: Sodium carbonate reacts with acids to produce corresponding salts, water, and carbon dioxide; reacts with alkalis such as calcium hydroxide to produce calcium carbonate precipitate and sodium hydroxide; reacts with certain calcium salts, barium salts, etc., to generate corresponding carbonate precipitates.
Product Application Fields:
Glass Manufacturing: Sodium carbonate is used to adjust the alkalinity during the glass melting process, helping to lower the softening point of glass and improve production efficiency.
Detergent Manufacturing: Sodium carbonate reacts with fatty acid salts in grease to produce soap, thereby removing grease.
Paper Industry: Sodium carbonate serves as a filler in paper, enhancing paper strength and whiteness.
Textile Industry: Sodium carbonate is used as a water softener to remove hardness ions from textile raw materials and finished products, reducing stains on fabrics.
Water Treatment: Sodium carbonate is used to adjust the pH of water and remove heavy metal ions and harmful substances.
Food Industry: Sodium carbonate acts as a leavening agent, reacting with acidic substances to produce carbon dioxide when baking bread, cookies, and other foods, making them fluffy. Additionally, it is used as a buffering agent, neutralizer, and dough improver.
Pharmaceutical Industry: Sodium carbonate is used as an antacid and osmotic laxative.
Metallurgical Industry: Sodium carbonate serves as a flux in smelting, a flotation agent in mineral processing, and a desulfurizing agent in steel and antimony refining.
Precautions:
Storage: Sodium carbonate should be stored in a cool, well-ventilated storeroom, away from fire and heat sources, and separately from acids to avoid mixing.
Operation: Sodium carbonate handling should be conducted in a closed environment with enhanced ventilation. Operators must be specially trained and strictly adhere to operating procedures. Operators are recommended to wear self-aspirating dust respirators, chemical safety glasses, anti-toxic permeable work clothes, and rubber gloves.
Environment: Although sodium carbonate can act as a buffer in the environment, maintaining the acid-base balance of water bodies and soil, large-scale discharges may affect the pH and total alkalinity of water bodies. Therefore, appropriate management and regulation are required during use and disposal.
In summary, sodium carbonate, as an important inorganic chemical raw material, plays a vital role in multiple fields. However, safety and environmental considerations must be taken into account when using and handling sodium carbonate.
Tel:
Email:1245771552@qq.com
Add:Zhanjie Industrial Park, Gongyi City, Henan Province, China