
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is a linear polymer with the chemical formula (C3H5NO) n. The following is a detailed introduction about polyacrylamide:
Product nature:
Physical state: It is a hard glassy solid at room temperature, and the product has various forms such as gel, latex, white powder particles, semi transparent beads, and flakes.
Solubility: It can dissolve in water in any proportion, and the aqueous solution is a uniform and transparent liquid. However, after long-term storage, the viscosity of the solution will decrease due to the slow degradation of the polymer.
Thermal stability: Good thermal stability.
Density: Approximately 1.302 g/cm ³ (23 ℃).
Product types and classifications:
Polyacrylamide can be classified into various types based on its structure and properties, including linear polyacrylamide, cross-linked polyacrylamide, non-ionic polyacrylamide, cationic polyacrylamide, anionic polyacrylamide, water-soluble polyacrylamide, and high molecular weight polyacrylamide. Different types of polyacrylamide have different characteristics and application fields.
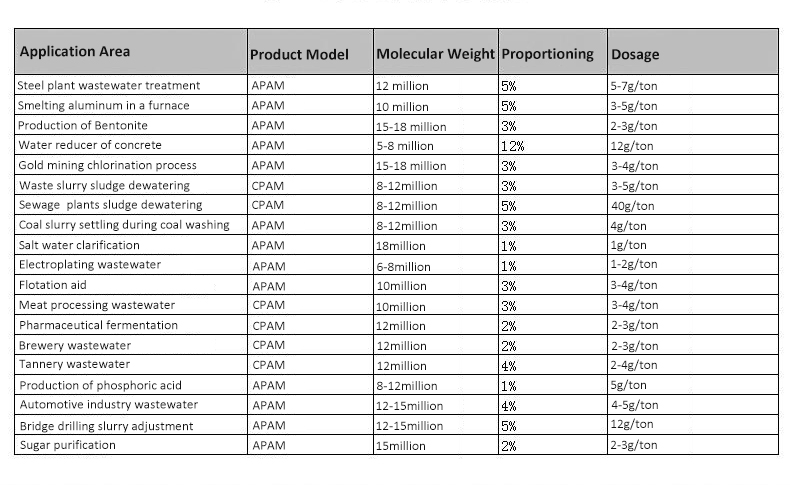
Product Dosage:
Product Features:
High molecular weight and solubility: Polyacrylamide has a high molecular weight and is soluble in water and other solvents, forming a transparent solution.
Water absorption: the modified polyacrylamide has good water absorption, which can absorb more than its own quality of water to form gel like substances.
Electrical properties: It exhibits ionicity in solution and can change its charge properties according to different conditions, possessing strong electroadsorption ability.
Polymer chain structure: Its molecules are composed of linear chain structures, which endow polyacrylamide with good tensile and tensile strength.
Stability: It can maintain good stability and is not easily affected by environmental factors such as acidity, alkalinity, salts, and high temperature.
Rheology: It has rheological properties and can be adjusted by controlling its molecular weight and structure to regulate its rheological behavior.
Product application areas:
Petroleum extraction: Polyacrylamide is used as an oil displacement agent and thickener in petroleum extraction to improve oil recovery efficiency.
Paper making: Polyacrylamide is used as a paper reinforcement and flocculant in the paper industry to improve the quality and stability of paper.
Water treatment: Polyacrylamide is used as a flocculant in water treatment to help remove suspended solids and impurities from water and improve water quality.
Textile: In the textile industry, polyacrylamide is used as a slurry and thickener to improve the performance of textiles.
Medicine: In the field of medicine, polyacrylamide is used to prepare drug carriers and sustained-release formulations.
Agriculture: Polyacrylamide is used as a soil amendment and plant growth regulator in agriculture to improve soil fertility and crop yield.
Product usage instructions:
1. Dissolution: It is recommended to use low hardness water with a neutral pH value for polyacrylamide dissolution. Avoid using wastewater, strong acids, strong bases, high salt content, and high temperature water. The stirring speed should be moderate to avoid prolonged and intense stirring that may cause product degradation.
2. Concentration configuration: The typical dissolution concentration for cationic products is 0.2%, while the dissolution concentration for anionic and non-ionic products is 0.1%. If there is a large amount of medication used in the on-site dissolution tank, the concentration should be slightly higher. When the molecular weight of polyacrylamide is high, the concentration should be slightly lower.
3. Addition: Polyacrylamide can be added through a metering pump, and the amount added needs to be adjusted according to the actual treatment process and water quality. During the addition process, attention should be paid to avoiding impact and shear to avoid affecting the stability and effectiveness of the solution.
4. Mixing: Polyacrylamide should be thoroughly mixed with water before addition to ensure uniform dispersion. At the same time, attention should be paid to the combination with other medications to achieve the best treatment effect.
5. Monitoring: Regular monitoring of water quality changes, such as COD, BOD, and other indicators, should be conducted after addition in order to adjust the dosage and treatment process in a timely manner.
Tel:
Email:1245771552@qq.com
Add:Zhanjie Industrial Park, Gongyi City, Henan Province, China