
Reverse osmosis scale inhibitors are specifically designed for use in reverse osmosis (RO) systems, as well as nanofiltration (NF) and ultrafiltration (UF) systems. They prevent scaling on membrane surfaces, enhance water production and quality, and reduce operational costs.
Product Classification:
Organic Scale Inhibitors: These are polymer-based chemicals that effectively prevent scaling on RO membrane surfaces through their unique molecular structures and mechanisms of action. Common organic scale inhibitors include polycarboxylic acids, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), and other polymers such as polyvinyl alcohol, polyvinyl alcohol esters, polyurethanes, polyvinyl chlorides, polyethylene glycols, hydroxyethyl celluloses, and epoxy resins. These inhibitors can effectively inhibit scaling on RO membrane surfaces within a wide concentration range, enhancing system performance and reliability.
Inorganic Scale Inhibitors: These inhibitors prevent scaling by reacting with inorganic salts in water to form soluble salts. Common inorganic scale inhibitors include inorganic acids such as sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and nitric acid, which react with alkaline and carbonate precipitates in water to form soluble salts, thereby preventing precipitates from accumulating on membrane surfaces. Additionally, inorganic oxides and salts such as phosphorus pentoxide, zinc oxide, iron oxide, alumina, and silicates are also widely used in reverse osmosis scale inhibition due to their antioxidant, corrosion-resistant, and scale-inhibiting properties.
Composite Scale Inhibitors: Composite scale inhibitors combine organic and inorganic inhibitors to achieve superior scale inhibition effects. These inhibitors combine the advantages of both organic and inorganic inhibitors, effectively inhibiting scaling on RO membranes through a comprehensive mechanism, enabling long-term stable operation of the RO system.
Product Features:
Effectively controls inorganic scaling within a wide concentration range;
Does not coagulate with iron and aluminum oxides and silicate compounds to form insoluble substances;
Effectively inhibits the polymerization and deposition of silicon, with SiO2 concentration on the concentrated water side up to 290;
Suitable for RO CA and TFC membranes, NF membranes, and UF membranes;
Excellent solubility and stability;
Effective in feed water with pH values ranging from 5 to 10.
Product Parameters:
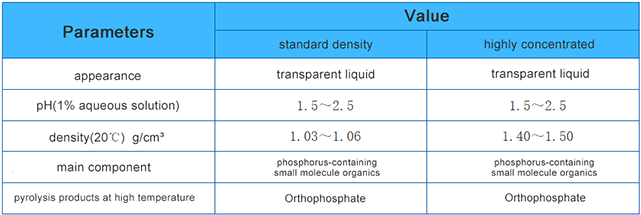
Product Functions:
Complexation and solubilization: The reverse osmosis scale inhibitor ionizes when dissolved in water, generating negatively charged molecular chains that form soluble complexes or chelates with Ca2+, thereby increasing the solubility of inorganic salts and providing scale inhibition.
Crystal lattice distortion: Some functional groups in the reverse osmosis scale inhibitor adsorb onto inorganic salt crystallites or microcrystallites, occupying certain positions and hindering and disrupting the normal growth of inorganic salt crystals, slowing down their growth rate and reducing the formation of scale.
Electrostatic repulsion: The reverse osmosis scale inhibitor adsorbs onto inorganic salt microcrystallites when dissolved in water, increasing the repulsive force between particles and preventing their aggregation, keeping them in a well-dispersed state and preventing or reducing the formation of scale.
Product Application Fields:
Power Industry: In water treatment systems of power plants and stations, reverse osmosis scale inhibitors are used to prevent the formation and accumulation of scale, ensuring the normal operation of water systems.
Food Industry: In the production processes of beverages, alcoholic beverages, and other products, reverse osmosis scale inhibitors are used to remove impurities and odors from water, improving product quality and taste.
Medical Industry: In hemodialysis, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and other fields, reverse osmosis scale inhibitors are used to remove bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms from water, ensuring medical safety and drug quality.
Environmental Protection Field: In wastewater treatment, seawater desalination, and other processes, reverse osmosis scale inhibitors effectively remove harmful substances from water, improving water quality and environmental quality.
Product Usage:
Thorough Mixing: Mix the reverse osmosis scale inhibitor and water proportionally until uniform.
Application of Scale Inhibitor: Introduce the mixed reverse osmosis scale inhibitor solution into the inlet pipeline of the membrane module through the dosing device or dosing pump of the RO system evenly.
Backwashing with Scale Inhibitor: After 5-10 minutes of dosing, the RO system begins backwashing, rinsing the scale inhibitor into the sludge tank or interceptor, ensuring no residual scale inhibitor in the membrane module.
Pipeline Cleaning: After backwashing, clean the dosing point to remove potential contaminants that may affect the membrane.
Inspection: Finally, inspect the cleaning effect of the membrane module and water quality to ensure that the use of the scale inhibitor achieves the expected results.
Precautions:
Compatibility Check: Before using the reverse osmosis scale inhibitor, confirm its compatibility with other pretreatment chemicals (such as flocculants, disinfectants, etc.) in the system. This is to avoid precipitation or chemical reactions between different chemicals, which may clog the RO membrane and affect system performance.
Reasonable Dosage Control: The rationality of the dosage directly relates to the scale inhibition effect and system operational efficiency. Too much or too little dosage may lead to membrane fouling. Therefore, it is necessary to precisely adjust the dosage based on the influent water quality, flow rate, temperature, and design parameters of the RO system.
Water Quality and System Monitoring: Regular monitoring of water quality and system performance is crucial for ensuring the effectiveness of the scale inhibitor. By monitoring indicators such as influent and product water quality, pressure difference, etc., potential problems can be identified and addressed promptly.
Correct Addition Method: The scale inhibitor should be added before the filter to ensure sufficient mixing and function before entering the RO membrane. At the same time, use a dedicated dosing tank and metering pump to ensure timed and quantitative addition. Before initial dosing, thoroughly clean the dosing tank to avoid contaminating the scale inhibitor.
Storage and Safety: Store reverse osmosis scale inhibitors in a dry, well-ventilated area, avoiding direct sunlight and rain. Operators should be familiar with the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) and take appropriate personal protective measures, such as wearing protective glasses and gloves.
Tel:
Email:1245771552@qq.com
Add:Zhanjie Industrial Park, Gongyi City, Henan Province, China